ASP.NET MVC - Using Ajax Helpers with Razor Partial Views
The case study presented in this guide uses one AjaxHelper class method to provide the asynchronous functionality needed to update a section of a web page without refreshing the entire page. Explore more now!
May 10, 2019 • 40 Minute Read
Introduction
Many web developers are challenged to design user interfaces that provide an interactive experience while collecting data from users and dynamically creating new page elements.
The collection of technologies known as AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) provides a way for web applications to asynchronously send and receive data from a server without the need to refresh the page or interfere with its appearance. By decoupling the presentational layer from the data exchange layer, AJAX (or Ajax) enables web applications to dynamically change content without reloading the entire page.
Ajax has enabled many enhancements to website user interfaces as support for Ajax has become more extensive in modern web browsers. Support for Ajax in the widely-used jQuery JavaScript library has simplified Ajax implementation.
Microsoft provides support for Ajax functionality in ASP.NET MVC through classes in the System.Web.Mvc and System.Web.Mvc.Ajax namespaces. One of the principal classes in this group is AjaxHelper<TModel> which, as Microsoft puts it, "includes methods that provide client-side functionality in ASP.NET AJAX in MVC applications, such as creating asynchronous forms and rendering links. The AjaxHelper class supports asynchronous partial-page updates."
The case study presented in this guide uses one AjaxHelper class method, BeginForm, to provide the asynchronous functionality needed to update a section of a web page without refreshing the entire page. The rest of the functionality comes from basic ASP.NET MVC components like controller actions and partial views.
Case Study Description
The examples shown in this guide are derived from a case study project available on GitHub. You can download and run the project to see the techniques illustrated here in action and to experiment on your own.
The case study is a multi-project Visual Studio 2017 solution developed from the default ASP.NET .NET Framework MVC template. It uses Entity Framework 6.1 and the repository and Model View ViewModel (MVVM) design patterns.
The solution consists of three projects that constitute the different layers of the application:
| Project | Application Layer |
|---|---|
| Blip.Data | Data Context and Repositories |
| Blip.Entities | Data Entities |
| Blip.Web | User Interface (views) and Business Logic (controllers) |
The case study application BlipAjax is a simple system for gathering, storing, and retrieving geographic and other information about customers. It's not production-ready from either the design or coding perspectives; it exists to illustrate the concepts discussed in this guide.
More importantly, Entity Framework and the repository and MVVM design patterns are production-ready tools. The example project was constructed so you can start with the MVC template and put together your own solutions using these resources using the sample project as a guide.
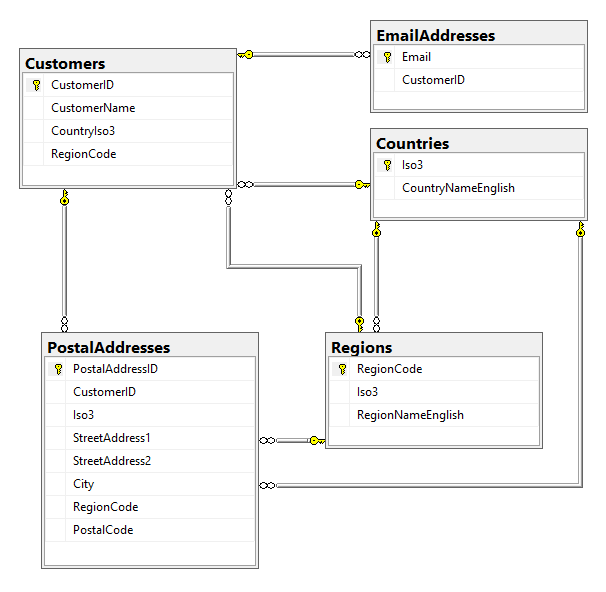
Entities
The structure of the BlipAjax entities is simple, there are customers, which are located in a specific country and region. They can have multiple e-mail addresses and multiple postal addresses. Postal addresses are similarly located in countries and regions. The entity-relationship diagram looks like this:
The Seed method of the Configuration class in Blip.Data.Migrations contains data for populating the lists of Countries and Regions.
Screenshots
The user interface for BlipAjax is as simple as the data model. Since the application is built on the MVC default template, the home page looks almost identical:
There is a new heading and button for the customer database functionality:
Selecting Edit at the end, for a customer, opens the customer edit page. It's this page that implements the Ajax functionality described in this guide.
The Address Type drop-down enables the user to select either "Email" or "Postal" address. When the user presses "Select", the Ajax HTTP POST functionality of the related partial view, AddressTypePartial.cshtml, is activated and the page is updated with either the partial view for creating an e-mail address, CreateEmailAddressPartial.cshtml, or CreatePostalAddressPartial.cshtml, the partial view for creating a postal address.
This is the Edit Customer Information view with the e-mail address option selected:
And this is what Edit Customer Information looks like with the postal address option selected:
Code Intro
ASP.NET MVC Ajax Helper classes provide functionality similar to that of a client-side framework without imposing the development overhead. With relatively little C#, a developer can create flexible, responsive user interface elements.
Components Summary
Separation of concerns and the constraint that HTML pages cannot have nested views both dictate that the Customer/Edit view cannot have its own view model. Instead, each form section of the view is composed of a partial view with its own view model.
In BlipAjax, the accompanying example solution, the application tiers are located in different projects, as follows:
| Application Tier | Project | Component |
|---|---|---|
| User Interface Presentation | Blip.Web | Views |
| User Interface Data | Blip.Entities | ViewModels |
| Business Logic | Blip.Web | Controllers |
| Data Entities | Blip.Entities | Models |
| Data Interface | Blip.Data | Repositories |
| Data Store | Blip.Data | Data Context |
Although there are a number files that comprise the single page Customer/Edit page, the relationship of the files is easy to discern.
View and Partial Views (.cshtml)
| Project | Folder |
|---|---|
| Blip.Web | Views/Customer |
| Component | File |
|---|---|
| Customer/Edit parent view | Edit.cshtml |
| Customer information partial view | EditCustomerPartial.cshtml |
| Address type selection partial view | AddressTypePartial.cshtml |
| E-mail address partial view | CreateEmailAddressPartial.cshtml |
| Postal address partial view | CreatePostalAddressPartial.cshtml |
Note that in the example application only one of the address partial views appears on the page at one time, either the e-mail partial view or the postal address partial view.
View Models Summary
| Project | Folder |
|---|---|
| Blip.Entities | Customers.ViewModels |
| Component | File |
|---|---|
| Customer/Edit parent view | (none) |
| Customer information partial view | CustomerEditViewModel.cs |
| Address type selection partial view | AddressTypeViewModel.cs |
| E-mail address partial view | EmailAddressViewModel.cs |
| Postal address partial view | PostalAddressEditViewModel.cs |
Controller Methods Summary
| Project | Folder | File |
|---|---|---|
| Blip.Web | Controllers/Customers | CustomerController.cs |
| Associated Partial View | Method | HTTP Action | Parameter(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Edit.cshtml | Edit | GET | string customerid |
| EditCustomerPartial.cshtml | EditCustomerPartial | GET | string customerid |
| EditCustomerPartial.cshtml | EditCustomerPartial | POST | CustomerEditViewModel |
| AddressTypePartial.cshtml | AddressTypePartial | GET | string customerid |
| AddressTypePartial.cshtml | AddressTypePartial | POST | AddressTypeViewModel |
| CreateEmailAddressPartial.cshtml | CreateEmailAddressPartial | POST | EmailAddressViewModel |
| CreatePostalAddressPartial.cshtml | CreatePostalAddressPartial | POST | PostalAddressEditViewModel |
Note that there is no signature associated with the Edit method. This is because all the HTTP POST activity associated with the Edit view takes place in the POST actions of the partial views:
- AddressTypePartial
- CreateEmailAddressPartial
- CreatePostalAddressPartial
Note also that CreateEmailAddressPartial and CreatePostalAddressPartial only have signatures for HTTP POST because the POST action of AddressTypePartial performs the function of invoking the Razor engine for the e-mail address and postal address partial views.
Views and Partial Views
Blip.Web/Views/Customer/Edit.cshtml
The code for the parent view is quite straightforward. Note the following:
-
There is no @model Razor directive: as noted in the code, the view models exist in the partial views.
-
The @Html.Action HtmlHelper is used to render two partial views when the Edit view is first rendered. The HtmlHelper invokes the corresponding HTTP GET action in CustomerController.cs.
-
The HTTP GET controller methods associated with the partial views require the current value of CustomerID to retrieve and return the appropriate data. This value is also the route value for the view, but it could also be passed in the ViewBag collection when the Edit view is called from the Index view. Judicious use of route values and data passed in the ViewBag or ViewData collections can serve the same function as data that might otherwise be bound in the data model.
-
An empty HTML element is used as the target for the Ajax action that renders either the e-mail address or postal address partial view.
<div id="CreateAddress"></div>
@*Models are in partial views.*@
@section header {
}
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Edit Customer Information";
}
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h2>Edit Customer Information</h2>
</div>
</div>
<div id="EditCustomerPartial">
@Html.Action("EditCustomerPartial", new { id = Url.RequestContext.RouteData.Values["id"] })
</div>
<div id="SelectAddressTypePartial">
@Html.Action("AddressTypePartial", new { id = Url.RequestContext.RouteData.Values["id"] })
</div>
<div id="CreateAddress"></div>
<div class="row">
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-12">
<hr />
<div>
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
@section Scripts {
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jqueryunobtrusive") @*For unobtrusive-ajax*@
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jqueryval") @*For validate and validate-unobtrusive*@
...
}
The JavaScript represented by the ellipses above provides functionality for the drop-down lists and does not effect the Ajax functionality. That topic is one for a separate tutorial. The complete code can be seen in the example project on GitHub.
JavaScript for AjaxHelper Methods
The Scripts section of Edit.cshtml contains a reference to a JavaScript bundle that is essential for the Ajax functionality. The jqueryunobtrusive bundle includes the script library jquery.unobtrusive-ajax.js (or jquery.unobtrusive-ajax.min.js in Release mode).
The jQuery library itself must be loaded before the unobtrusive-ajax library. This is done by this portion of the _Layout.cshtml shared view:
...
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jquery")
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/bootstrap")
@RenderSection("scripts", required: false)
...
Including the reference to ~/bundles/jqueryunobtrusive in the scripts section of the Edit.cshtml page ensures the Ajax library gets loaded after the jQuery library and only gets loaded on the page where it is used.
Blip.Web/Views/Customer/EditCustomerPartial.cshtml
Aside from being a partial view, EditCustomerPartial.cshtml contains all the standard features of a data-driven Razor view:
-
A model bound with the @model Razor directive.
-
An HTML form section created with the HtmlHelper.BeginForm method.
Note that the signature used identifies the partial view, controller name, and HTTP form method.
-
Form controls bound to the view model.
-
A submit button for the form.
Note that it also has a code section where the value of the Layout attribute of the view is set to null. This addresses a problem where in which the Razor rendering engine can apply all the features of the _Layout.cshtml file, usually found in the Shared folder, to partial views when the first partial view encountered has a bound data model but the parent view does not. Setting this value to null forces the Razor engine to render the partial view as a partial view.
@model Blip.Entities.Customers.ViewModels.CustomerEditViewModel
@{
Layout = null;
}
@using (Html.BeginForm("EditCustomerPartial", "Customer", FormMethod.Post))
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-horizontal">
<hr />
<h4>Edit customer details</h4>
@Html.ValidationSummary(true, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.CustomerID, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.CustomerID, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control", @readonly = "readonly" } })
</div>
</div>
...
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Save" class="btn btn-primary" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
Because the submit button is associated with the HTML form defined in this partial view, its action and the data associated with it are specific to this <form> element within the page.
Blip.Web/Views/Customer/AddressTypePartial.cshtml
The partial view for selecting the address type to add (e-mail or postal) is also simple and is, for the most part, similar to a conventional data-backed view. The important differences are in how the <form> element is generated and, as a result, what happens with the submit button is pressed.
-
The HTML <form> element is generated with the Ajax.BeginForm helper method rather than an Html.BeginForm helper method.
-
The first argument, "AddressTypePartial", identifies the partial view that contains the form.
-
The second argument consists of an AjaxOptions object with the following properties:
| Property | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| HttpMethod | POST | The HTTP action that will occur when the submit button is pressed. |
| UpdateTargetId | CreateAddress | The element of the parent form (Edit.cshtml) to be acted on by the result of the POST action. |
| InsertionMode | InsertionMode.Replace | What will be done with the results of the POST action in relation to the target element. |
@model Blip.Entities.Customers.ViewModels.AddressTypeViewModel
@using (Ajax.BeginForm("AddressTypePartial", new AjaxOptions { HttpMethod = "POST", UpdateTargetId = "CreateAddress", InsertionMode = InsertionMode.Replace }))
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-horizontal">
<hr />
<h4>Select an address type to add</h4>
@Html.ValidationSummary(true, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.CustomerID)
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.SelectedAddressType, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2", id="AddressTypeLabel" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.DropDownListFor(model => model.SelectedAddressType, new SelectList(Model.AddressTypes, "Value", "Text"), htmlAttributes: new { @class = "form-control", id="AddressType" } )
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.SelectedAddressType, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Select" class="btn btn-primary" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
Note that an Html.AntiForgeryToken() method call is included for each partial view.
Also note that neither partial view contains JavaScript. Scripts are located in the parent form, with one exception discussed in the companion tutorial on using JavaScript with Ajax partial views.
Rendered HTML
The generated HTML rendered by the browser for the Customer/Edit view appears below. It is worth studying the client-side HTML closely because doing so makes the relationship between the partial views, the <form> elements, and the controller actions clearer.
Note the following features of the HTML:
-
There are two <form> elements, one each in the elements corresponding to the partial views: <div id="EditCustomerPartial"> <div id="SelectAddressTypePartial">
-
Each form has an anti-forgery token.
-
Each form has a HTTP POST action that points to the controller method signature corresponding to the POST method for the associated partial view.
-
The SelectAddressTypePartial form element includes Ajax attributes that specify the actions to perform when the POST action returns from the server, including specifying the replacement of the CreateAddress element.
-
The <div id="CreateAddress"></div> element exists within the <body> element, but outside either of the <form> elements.
-
The <script> includes at the bottom of the page include jquery-3.2.1.js and jquery.unobtrusive-ajax.js, the two libraries essential for the AjaxHelper classes.
Ellipsis (...) indicates code has been redacted for brevity.
localhost:61621/Customer/Edit/68f8202d-21cb-4090-a86c-0722bf588d1b
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Edit Customer Information - My ASP.NET Application</title>
<link href="/Content/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet"/>
<link href="/Content/site.css" rel="stylesheet"/>
<script src="/Scripts/modernizr-2.8.3.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="navbar navbar-inverse navbar-fixed-top">
...
</div>
<div class="container body-content">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h2>Edit Customer Information</h2>
</div>
</div>
<div id="EditCustomerPartial">
<form action="/Customer/EditCustomerPartial/68f8202d-21cb-4090-a86c-0722bf588d1b" method="post">
<input name="__RequestVerificationToken" type="hidden" value="rN4xA8UDIHeo8YHYFZ4Bnc16Fr6oQdjpnV0hKPNpgHcMHNe5ZyE7tCP5ouWG3OyRGI8a9ihfpoaonfd1pf5o-RcQuG7049hNX0cKSTuNE0I1" />
<div class="form-horizontal">
<hr />
<h4>Edit customer details</h4>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="control-label col-md-2" for="CustomerID">Customer Number</label>
<div class="col-md-10">
<input class="form-control text-box single-line" id="CustomerID" name="CustomerID" readonly="readonly" type="text" value="68f8202d-21cb-4090-a86c-0722bf588d1b" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="control-label col-md-2" for="CustomerName">Customer Name</label>
<div class="col-md-10">
<input class="form-control text-box single-line" data-val="true" data-val-length="The field Customer Name must be a string with a maximum length of 75." data-val-length-max="75" data-val-required="The Customer Name field is required." id="CustomerName" name="CustomerName" type="text" value="Spacely Space Sprokets" />
<span class="field-validation-valid text-danger" data-valmsg-for="CustomerName" data-valmsg-replace="true"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="control-label col-md-2" for="SelectedCountryIso3">Country</label>
<div class="col-md-10">
<select class="form-control" data-val="true" data-val-required="The Country field is required." id="Country" name="SelectedCountryIso3">
<option value="">--- select country ---</option>
<option value="CAN">Canada</option>
<option value="FRA">France</option>
<option selected="selected" value="USA">United States of America</option>
</select>
<span class="field-validation-valid text-danger" data-valmsg-for="SelectedCountryIso3" data-valmsg-replace="true"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="control-label col-md-2" for="SelectedRegionCode">State / Region</label>
<div class="col-md-10">
<select class="form-control" data-val="true" data-val-required="The State / Region field is required." id="Region" name="SelectedRegionCode">
<option value="AL">Alabama</option>
<option value="AK">Alaska</option>
...
<option value="WY">Wyoming</option>
</select>
<span class="field-validation-valid text-danger" data-valmsg-for="SelectedRegionCode" data-valmsg-replace="true"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Save" class="btn btn-primary" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<div id="SelectAddressTypePartial">
<form action="/Customer/AddressTypePartial/68f8202d-21cb-4090-a86c-0722bf588d1b" data-ajax="true" data-ajax-method="POST" data-ajax-mode="replace" data-ajax-update="#CreateAddress" id="form0" method="post">
<input name="__RequestVerificationToken" type="hidden" value="w6veexTOKQxJc3_3BQh7yRC7mHM-iSQgkXaIQdh3EZsTVELEnsxpgpYtSSpZ4CO0ZZdfQrEjck8UBomFrTcHfJuH343y1n1eWv_OmDCjAUE1" />
<div class="form-horizontal">
<hr />
<h4>Select an address type to add</h4>
<input data-val="true" data-val-length="The field CustomerID must be a string with a maximum length of 38." data-val-length-max="38" id="CustomerID" name="CustomerID" type="hidden" value="68f8202d-21cb-4090-a86c-0722bf588d1b" />
<div class="form-group">
<label class="control-label col-md-2" for="SelectedAddressType" id="AddressTypeLabel">Address Type</label>
<div class="col-md-10">
<select class="form-control" id="AddressType" name="SelectedAddressType">
<option value="Email">Email</option>
<option value="Postal">Postal</option>
</select>
<span class="field-validation-valid text-danger" data-valmsg-for="SelectedAddressType" data-valmsg-replace="true"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Select" class="btn btn-primary" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<div id="CreateAddress"></div>
<div class="row">
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-12">
<hr />
<div>
<a href="/Customer">Back to List</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
...
<script src="/Scripts/jquery-3.2.1.js"></script>
<script src="/Scripts/bootstrap.js"></script>
<script src="/Scripts/respond.js"></script>
<script src="/Scripts/jquery.unobtrusive-ajax.js"></script>
<script src="/Scripts/jquery.validate.js"></script>
<script src="/Scripts/jquery.validate.unobtrusive.js"></script>
...
</body>
</html>
Customer/Edit Ajax Response
When "Email" is selected for Address Type and the Select button is pressed, the CreateAddress <div> is replaced with the following code:
<div id="CreateAddress">
<form action="/Customer/CreateEmailAddressPartial" method="post"><input name="__RequestVerificationToken" type="hidden" value="p3BCpdqspecbfFOxrQfzdrt9cyoiVgtloMzHDYUbYgmeVbEssngLCmfWTUGGY0p8sWGzOFex1PURQDZCctvoteNvTBeDVfUgPJ8CrebXxl41" /> <div class="form-horizontal">
<hr />
<h4>Add a new Email Address</h4>
<input data-val="true" data-val-length="The field CustomerID must be a string with a maximum length of 38." data-val-length-max="38" id="CustomerID" name="CustomerID" type="hidden" value="68f8202d-21cb-4090-a86c-0722bf588d1b" />
<div class="form-group">
<label class="control-label col-md-2" for="Email">Email</label>
<div class="col-md-10">
<input class="form-control text-box single-line" id="email" name="Email" type="email" value="" />
<span class="field-validation-valid text-danger" data-valmsg-for="Email" data-valmsg-replace="true"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input id="AddButton" type="submit" value="Add" class="btn btn-primary" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
This adds a third <form> element to the page with its own submit button. Selecting "Postal" in the Address Type drop-down and pressing Select adds the corresponding partial view for adding a postal address.
Each form interacts with its own controller methods, as do the forms for editing customer information and selecting the type of address to add (e-mail or postal). Accordingly, updated information about the customer can be added using the first form on the page independent of the submission of the e-mail address or postal address information.
Controller Actions
Looking at the CustomerController.cs methods will provide a more complete understanding of how each section of of the Customer/Edit view works and how Ajax is used to update the view with new content without refreshing the entire page.
The following table summarizes the elements of the view and the controller methods with which they interact:
| View | ViewModel | Form Helper Type | HTTP Action | Controller Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edit.cshtml | (none) | (none) | GET | ActionResult Edit(string id) |
| EditCustomerPartial.cshtml | CustomerEditViewModel.cs | HTML | GET | ActionResult EditCustomerPartial(string id) |
| EditCustomerPartial.cshtml | CustomerEditViewModel.cs | HTML | POST | ActionResult EditCustomerPartial(CustomerEditViewModel model) |
| AddressTypePartial.cshtml | AddressTypeViewModel.cs | Ajax | GET | ActionResult AddressTypePartial(string id) |
| AddressTypePartial.cshtml | AddressTypeViewModel.cs | Ajax | POST | ActionResult AddressTypePartial(AddressTypeViewModel model) |
| CreateEmailAddressPartial.cshtml | EmailAddressViewModel.cs | HTML | POST | ActionResult CreateEmailAddressPartial(EmailAddressViewModel model) |
| CreatePostalAddressPartial.cshtml | PostalAddressEditViewModel.cs | HTML | POST | ActionResult CreateEmailAddressPartial(PostalAddressEditViewModel model) |
Note that there is no POST method for the Edit parent view because all the forms and submit buttons belong to partial views and each has its own associated controller methods.
Note also that there are no HTTP GET actions for the e-mail address and postal address partial views. These views are rendered by the POST action signature of the AddresTypePartial method.
Edit View GET Method
Rendering the view begins with an ActionResult method for Edit.cshtml, the parent page. Note that there is no view model associated with this view; as described above, all the related view models are associated with the partial views. All that this view needs to to is check for a valid GUID and return the view.
// GET: Customer/Edit/68f8202d-21cb-4090-a86c-0722bf588d1b
public ActionResult Edit(string id)
{
if (!String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(id))
{
bool isGuid = Guid.TryParse(id, out Guid customerId);
if (isGuid && customerId != Guid.Empty)
{
return View();
}
}
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
EditCustomerPartial GET Method
This method is called during the rendering of Edit.cshtml by this line in the Razor view:
@Html.Action("EditCustomerPartial", new { id = Url.RequestContext.RouteData.Values["id"] })
Note that the Html.Action helper method passes the route value for the CustomerID as an argument. The value of id is used to retrieve the customer record from the SQL Server database using the GetCustomer method of CustomersRepository.
The customer information is returned in an instance of CustomerEditViewModel, which provides the values for the drop-down lists for Country and Region as well as the current values for the country and region associated with the customer record. This is all handled by the repository so the business logic doesn't have to be concerned with the data needed for mechanizing the user interface.
``csharp [ChildActionOnly] public ActionResult EditCustomerPartial(string id) { if (!String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(id)) { bool isGuid = Guid.TryParse(id, out Guid customerId); if (isGuid && customerId != Guid.Empty) { var repo = new CustomersRepository(); var model = repo.GetCustomer(customerId); return View(model); } } return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest); }
The method is decorated with the `ChildActionOnly` attribute to indicate that it can only be called within a parent view, never as a standalone GET action. This prevents the partial view from being rendered on its own and potentially being used to subvert the proper operation of the application.
#### AddressTypePartial GET Method
This method is called during the rendering of **Edit.cshtml** by this line in the Razor view:
`@Html.Action("AddressTypePartial", new { id = Url.RequestContext.RouteData.Values["id"] })`
As with the partial view for editing customer information, this GET method populates the data in the view model that supports the user interface.
```csharp
[ChildActionOnly]
public ActionResult AddressTypePartial(string id)
{
if (!String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(id))
{
bool isGuid = Guid.TryParse(id, out Guid customerId);
if (isGuid && customerId != Guid.Empty)
{
var repo = new MetadataRepository();
var model = new AddressTypeViewModel()
{
CustomerID = id,
AddressTypes = repo.GetAddressTypes()
};
return PartialView("AddressTypePartial", model);
}
}
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
At this point, the Razor engine has all the data and markup it needs to render the page. The Customer/Edit view can be used by the user.
AddressTypePartial POST Method
When the user selects an address type to add and presses the Select button, the data is sent to the server and handled by the POST method for AddressTypePartial. This method will not execute unless the anti-forgery token associated with the form is valid.
HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult AddressTypePartial(AddressTypeViewModel model)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid && !String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(model.CustomerID))
{
switch (model.SelectedAddressType)
{
case "Email":
var emailAddressModel = new EmailAddressViewModel()
{
CustomerID = model.CustomerID
};
return PartialView("CreateEmailAddressPartial"
Depending on the type of address selected by the user, this method creates an instance of the appropriate view model and sets the value of CustomerID. If the postal address type is selected, the controller also populates the relevant SelectList collections for the lists of countries and regions. The controller then returns the appropriate view along with the associated view model.
On the client side, the browser takes the HTML and data from the server and, using the JavaScript libraries, renders the partial view and its view model data in place of the <div id="CreateAddress"> element.
At this point, the user can enter and submit data for the selected address type, or re-select the address type and see the page updated with the other partial view. Once the user enters data and presses the Save button, the appropriate POST controller method handles the request.
CreateEmailAddressPartial POST Method
In the case of an e-mail address, the POST method looks like this. It is a simple matter of using the repository to save the data and responding accordingly to the results of that method call.
HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult CreateEmailAddressPartial(EmailAddressViewModel model)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
var repo = new CustomersRepository();
bool saved = repo.SaveEmailAddress(model);
if (saved)
{
return RedirectToAction("Edit"
In the example project, when the e-mail address is successfully saved, the controller passes control to the method to load the Customer/Edit page (Edit.cshtml) for the current customer. This is equivalent to resetting the page. In real-world applications, any number of other results are possible, including reloading an Ajax partial view that displays the current list of addresses of the associated type.
Other Ajax Actions
In addition to adding a new form to a page, the Ajax.BeginForm helper can be used to create Ajax functionality to perform other useful actions. The actionName, controllerName, and routeValues parameters can be used to access controller actions from a specific controller and pass a variety of data to the controller.
In addition, the AjaxOptions parameter can be used to define what happens with the partial view as it is being added to the page. Some of the options are:
InsertionMode - defines whether the new <form> element replaces the identified element or is added before or after the existing element. This is useful when building a list of items on the page as the user adds information.
OnBegin - can set the JavaScript function to call before the <form> element is added.
OnSuccess - can set the JavaScript function to call when the <form> has finished loading.
Conclusion
ASP.NET MVC AjaxHelper methods provide a flexible way to add Ajax functionality to Razor views. In many cases this can provide the desired functionality without the resource commitment and potential learning curve associated with implementing a client-side framework like Angular.
Ajax helper methods leverage the developer's knowledge of server-side programming with C# and with the MVC design pattern. They require minimal code in the Razor view and allow for powerful combinations of partial views, controller actions, and client-side JavaScript to create an interactive single page experience for the user.
Implementing the Model View ViewModel (MVVM) design pattern by combining Ajax helpers with partial views and associated view models can provide an effective separation of concerns for interactive pages built with these resources. Compatibility of ASP.NET security tools like the anti=forgery token with Ajax helpers ensures the robust security of ASP.NET without additional programming effort.
Developers should evaluate the capabilities of AjaxHelper methods before deciding to move from ASP.NET MVC to WebAPI and Angular (or another client-side framework). This is particularly true when search engine optimization (SEO) and page analytics integration are objectives.
More Information
If you want to dive deeper into the topics discussed in this guide or experiment with the code shown above, the following is a selected list of resources.
Example Project
The complete Visual Studio solution described in this guide is available on GitHub: BlipAjax
The example project is provided as is, without any warranty expressed or implied. Neither Pluralsight nor the author is responsible for any errors or omissions.
ASP.NET MVC Advanced Topics by Scott Allen, 22 July 2009. The first module of this course, Ajax with ASP.NET MVC, provides a nice narrated overview of the related technology.
Other Resources
Disclaimer: Pluraldight and the author of this guide are not responsible for the content, accuracy, or availability of third party resources.
Microsoft: System.Web.Mvc.Ajax namespace - This is the canonical documentation for the AjaxExtensions (including the BeginForm method) and AjaxOptions classes. Note that if you go looking for information on docs.microsoft.com it will boot you over to this URL. Although this page refers to Visual Studio 2013, it is, in fact, the most recent documentation.
Wikipedia: Ajax (programming) - A nice summary of the Ajax architecture, history, and implementation. Good background for beginners looking for a fundamental grounding in the technology.
Advance your tech skills today
Access courses on AI, cloud, data, security, and more—all led by industry experts.