Making a Notes App Using Room Database
Learn how to build an Android note app with room database. Learn what storage options there for your Android database and the basics of room database.
Jan 10, 2019 • 25 Minute Read
Introduction
Data persistence is one of the basic requirements of most applications. SQLite, an open-source library is a means of persisting data for Android applications. The implementation of SQLite requires lots of boilerplate code, however. This has drawbacks:
- Syntax errors in queries
- No compile time error detection (Time consuming)
- Parsing is required to convert data to Plain Old Java Objects (POJO) objects
These issues are quite common in Q&A forums, which is likely why popular No-SQL databases like Realm, GreenDAO and Room came along. Room is a persistent library that abstract away the most of the SQLite code using annotations.
** This tutorial aims to cover: **
- Storage options for Android
- SQL vs. No-SQL
- Room Library basics
- Using the Room Library to build a notepad app
Introduction to Android storage mechanisms
Core data storage mechanisms
- Key-Value pairs : SharedPreferences, An android framework API, which stores key-values pairs in an XML file under protected file system.
- Data stored via SharedPreference can only be accessed within the app.
- Can only store boolean, int, long, String and Set of String.
-
Internal and External storage : Applications can store text or CSV files, images, videos in phone memory or inside public directories(kitkat or above) under SD card storage.
- To access phone or external storage, Applications requires to implement Requesting Permissions Model for marshmallow and above.
- Repeatedly accessing physical hard drive space slows down the application.
- Applications can access all directories under external storage on API's below KitKat.
- Accessible to other applications, No protection.
-
SQLite : SQLite is a light-weight relational database, embedded into the Android OS. The database schema is mapped to tables and integrity constraints.
-
NoSQL : NoSQL simply means Objects or Documents. Instead of storing the data in tabular form, The data is stored in POJO form, which is extremely suitable for semi-structured or un-structured data when there is no fixed schema.
SQL vs NoSQL
| Features | SQL | No-SQL |
|---|---|---|
| Data Stored | In Tabular form (RDBMS) | POJO objects or Documents |
| Data Manipulation | via DML,DDL | via provided API's |
| Structure | RDBMS | key-value pairs |
| Schema | Fixed schema | dynamic, records can be added on the fly |
| Scalable | RDBMS | key-value pairs |
| Android Support | SQLite | Room(semi-sql), GreenDAO, Realm |
Room Basics
The Room library acts as an abstract layer for underlying SQLite database. Thus, Room annotations are used:
- To Database and Entities where entities are POJO classes representing table structures.
- To specify operation for retrieval, updation and deletion.
- To add constraints, such as foreign keys.
- Support for LiveData.
There are 3 major components in Room
- Entity : A class annotated with the @Entity annotation is mapped to a table in database. Every entity is persisted in its own table and every field in class represents the column name.
- tableName attribute is used to define the name of the table
- Every entity class must have at-least one Primary Key field, annotated with @PrimaryKey
- Fields in entity class can be annotated with @ColumnInfo(name = “name_of_column”) annotation to give specific column names
-
DAO : Data Access Object is either be an interface or an abstract class annotated with @Doa annotation, containing all the methods to define the operations to be performed on data. The methods can be annotated with
-
Database : Database is a container for tables. An abstract class annotated with @Database annotation is used to create a database with given name along with database version.
- version = intValueForDBVersion is used to define the database version
- entities = {EntityClassOne.class, ....} is used to define list of entities for database
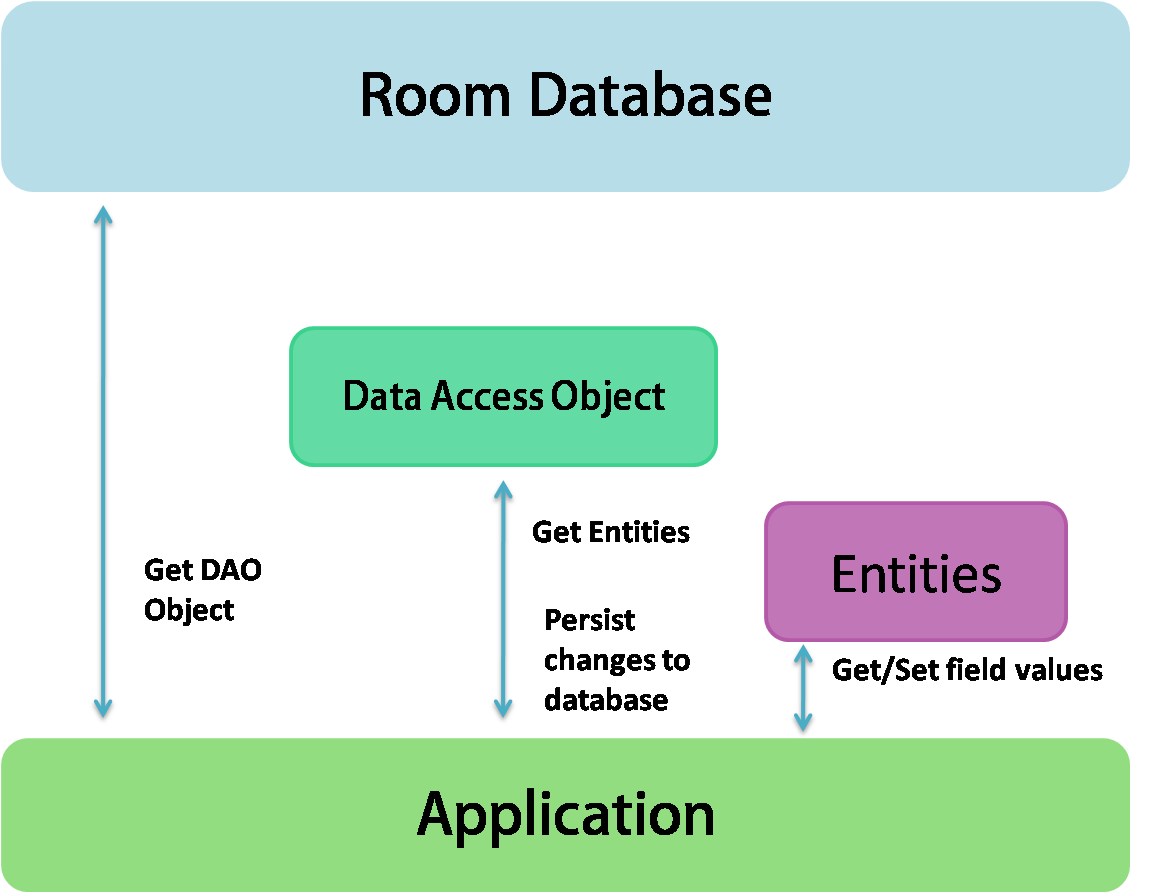
Room Architecture
Building a Notepad App
Hopefully, you are tempted enough to try Room library now! We will build a Notes App that will allow the user to:
- Create and Save notes in database
- Display a list of notes
- Update and Delete notes
The demo application we create here will hopefully demonstrate database-oriented application skills and get you started with Room. Conceptually, however, this code can further be extended or changed to build alarm apps, scheduling apps, SMS-driven applications, and more.
All the code is available at Github Repo
Getting Started
Create a new project in Android Studio. Choose "Basic Activity" template.
Add a Maven Repository
Next, add a Maven Repository. Open build.gradle project and add following Maven dependency
allprojects {
repositories {
google()
jcenter()
maven {
url "https://maven.google.com"
}
}
}
Google Maven Repository provides all the updated support libraries, which will be downloaded by gradle instead of downloading from SDK Manager.
Then we will add a Room dependency in build.gradle(Module:app) within the dependency block.
dependencies {
//... other dependencies
// Room dependencies
compile 'android.arch.persistence.room:runtime:1.0.0'
annotationProcessor 'android.arch.persistence.room:compiler:1.0.0'
}
Create Entity
Before creating a database, Let's create an Entity, named as Note and later, Objects of this class will be added to database.
To do this:
- Create a class named Note.
- Add @Entity annotation on the class.
- Add ID, content, and title fields.
- Important: mark at least one field with @PrimaryKey annotation.
- Use alt+insert to implement constructor, override getter and setter, and optionally override equals or toString.
package com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo.notedb.model;
import android.arch.persistence.room.Entity;
import android.arch.persistence.room.PrimaryKey;
@Entity
public class Note {
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)
private int note_id;
@ColumnInfo(name = "note_content") // column name will be "note_content" instead of "content" in table
private String content;
private String title;
private
public Note(int note_id, String content, String title) {
this.note_id = note_id;
this.content = content;
this.title = title;
}
public int getNote_id() {
return note_id;
}
public void setNote_id(int note_id) {
this.note_id = note_id;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Note)) return false;
Note note = (Note) o;
if (note_id != note.note_id) return false;
return title != null ? title.equals(note.title) : note.title == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = note_id;
result = 31 * result + (title != null ? title.hashCode() : 0);
return result;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Note{" +
"note_id=" + note_id +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Creating DAOs
DAOs define all methods to access database, annotated with @Dao annotation. The DAO acts as a contract to perform CRUD operations on data within a database.
The following code will:
- Create an interface, marked with @Dao annotation.
- Add methods for CURD operations.
package com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo.notedb.dao;
import android.arch.persistence.room.Dao;
import android.arch.persistence.room.Delete;
import android.arch.persistence.room.Insert;
import android.arch.persistence.room.Query;
import android.arch.persistence.room.Update;
import com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo.notedb.model.Note;
import com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo.util.Constants;
import java.util.List;
@Dao
public interface NoteDao {
@Query("SELECT * FROM user "+ Constants.TABLE_NAME_NOTE)
List<Note> getAll();
/*
* Insert the object in database
* @param note, object to be inserted
*/
@Insert
void insert(Note note);
/*
* update the object in database
* @param note, object to be updated
*/
@Update
void update(Note repos);
/*
* delete the object from database
* @param note, object to be deleted
*/
@Delete
void delete(Note note);
/*
* delete list of objects from database
* @param note, array of objects to be deleted
*/
@Delete
void delete(Note... note); // Note... is varargs, here note is an array
}
Create Database
Now, we have table defined as Entity and CRUD methods defined via NoteDao. The last piece of the database puzzle is the database itself.
We will have to:
- Create an abstract class NoteDatabse which extends RoomDatabase.
- Add version and entities to database as @Database(entities = {Note.class}, version = 1).
- Add abstract methods of all DAO's where the returned DAO object will be constructed by Room for database interactions.
Some things to remember:
- Version number is changed to update the database structure, when required in future updates
- The database file name must end with the .db extension
- Creating instance of database is quite costly so we will apply a Singleton Pattern to create and use already instantiated single instance for every database access.
package com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo.notedb;
import android.arch.persistence.room.Database;
import android.arch.persistence.room.Room;
import android.arch.persistence.room.RoomDatabase;
import android.content.Context;
import com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo.notedb.dao.NoteDao;
import com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo.util.Constants;
@Database(entities = { Note.class }, version = 1)
public abstract class NoteDatabase extends RoomDatabase {
public abstract NoteDao getNoteDao();
private static NoteDatabase noteDB;
public static NoteDatabase getInstance(Context context) {
if (null == noteDB) {
noteDB = buildDatabaseInstance(context);
}
return noteDB;
}
private static NoteDatabase buildDatabaseInstance(Context context) {
return Room.databaseBuilder(context,
NoteDatabase.class,
Constants.DB_NAME)
.allowMainThreadQueries().build();
}
public void cleanUp(){
noteDB = null;
}
}
Additionally, it is good to note that Room does not allow code execution on Main thread. Instead, allowMainThreadQueries is used to allow the execution. However, using this is not recommended on real apps. This is just for demonstration instead use AsyncTask (or handler, rxjava). The AddNoteActivity.java snippet demonstrates how to use AsyncTask.
Implement Database Interactions
The below snippet will demonstrate the working of insert, update, and delete functionality using the Room database.
Add Notes
In AddNoteActivity.java
- Initialize views and database.
- Fetch data from EditText and create Note object.
- Insert previously created Note object into database.
package com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.design.widget.TextInputEditText;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo.notedb.NoteDatabase;
import com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo.notedb.model.Note;
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
public class AddNoteActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextInputEditText et_title,et_content;
private NoteDatabase noteDatabase;
private Note note;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_add_note);
et_title = findViewById(R.id.et_title);
et_content = findViewById(R.id.et_content);
noteDatabase = NoteDatabase.getInstance(AddNoteActivity.this);
Button button = findViewById(R.id.but_save);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// fetch data and create note object
note = new Note(et_content.getText().toString(),
et_title.getText().toString());
// create worker thread to insert data into database
new InsertTask(AddNoteActivity.this,note).execute();
}
});
}
private void setResult(Note note, int flag){
setResult(flag,new Intent().putExtra("note",note));
finish();
}
private static class InsertTask extends AsyncTask<Void,Void,Boolean> {
private WeakReference<AddNoteActivity> activityReference;
private Note note;
// only retain a weak reference to the activity
InsertTask(AddNoteActivity context, Note note) {
activityReference = new WeakReference<>(context);
this.note = note;
}
// doInBackground methods runs on a worker thread
@Override
protected Boolean doInBackground(Void... objs) {
activityReference.get().noteDatabase.getNoteDao().insertNote(note);
return true;
}
// onPostExecute runs on main thread
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(Boolean bool) {
if (bool){
activityReference.get().setResult(note,1);
}
}
}
}
activity_add_note.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="4dp"
tools:context="com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo.AddNoteActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout
android:id="@+id/txtInput"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputEditText
android:inputType="text"
android:id="@+id/et_title"
android:hint="Title"
android:singleLine="true"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_below="@+id/txtInput"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout
android:id="@+id/txtInput2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="0dp">
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputEditText
android:id="@+id/et_content"
android:hint="Content"
android:gravity="top"
android:singleLine="false"
android:inputType="textMultiLine|textNoSuggestions"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/but_save"
android:text="Save"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
Visual result of AddNoteActivity with above implementation
Retrieve And Display NoteList
- Initialize Room database instance and fetch all note objects as List.
- To display list, we will use RecyclerView.
- Pass the list of notes to adapter and link adapter with the RecyclerView.
NoteListActivity.java
package com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton;
import android.support.v7.app.AlertDialog;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.support.v7.widget.LinearLayoutManager;
import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView;
import android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo.adapter.NotesAdapter;
import com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo.notedb.NoteDatabase;
import com.example.pavneet_singh.roomdemo.notedb.model.Note;
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
import java.util.List;
public class NoteListActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements NotesAdapter.OnNoteItemClick{
private TextView textViewMsg;
private RecyclerView recyclerView;
private NoteDatabase noteDatabase;
private List<Note> notes;
private NotesAdapter notesAdapter;
private int pos;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initializeVies();
displayList();
}
private void displayList(){
// initialize database instance
noteDatabase = NoteDatabase.getInstance(NoteListActivity.this);
// fetch list of notes in background thread
new RetrieveTask(this).execute();
}
private static class RetrieveTask extends AsyncTask<Void,Void,List<Note>>{
private WeakReference<NoteListActivity> activityReference;
// only retain a weak reference to the activity
RetrieveTask(NoteListActivity context) {
activityReference = new WeakReference<>(context);
}
@Override
protected List<Note> doInBackground(Void... voids) {
if (activityReference.get()!=null)
return activityReference.get().noteDatabase.getNoteDao().getNotes();
else
return null;
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(List<Note> notes) {
if (notes!=null && notes.size()>0 ){
activityReference.get().notes = notes;
// hides empty text view
activityReference.get().textViewMsg.setVisibility(View.GONE);
// create and set the adapter on RecyclerView instance to display list
activityReference.get().notesAdapter = new NotesAdapter(notes,activityReference.get());
activityReference.get().recyclerView.setAdapter(activityReference.get().notesAdapter);
}
}
}
private void initializeVies(){
Toolbar toolbar = (Toolbar) findViewById(R.id.toolbar);
setSupportActionBar(toolbar);
textViewMsg = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv\_\_empty);
// Action button to add note
FloatingActionButton fab = (FloatingActionButton) findViewById(R.id.fab);
fab.setOnClickListener(listener);
recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.recycler_view);
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(NoteListActivity.this));
}
}
Update Note
To update note object, the content of already created object needs to be updated while keeping the same primary key
- Receive the Note Object from NoteListActivity and display its content on screen
- Once the data has been updated by user, fetch the updated version from EditText and update the note object.
- Invoke update method of NoteDao with a Room database instance and pass in the updated note object.
Here, AddNoteActivity is being reused to perform update and insertion.
public class AddNoteActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextInputEditText et_title,et_content;
private NoteDatabase noteDatabase;
private Note note;
private boolean update;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_add_note);
et_title = findViewById(R.id.et_title);
et_content = findViewById(R.id.et_content);
noteDatabase = NoteDatabase.getInstance(AddNoteActivity.this);
Button button = findViewById(R.id.but_save);
if ( (note = (Note) getIntent().getSerializableExtra("note"))!=null ){
getSupportActionBar().setTitle("Update Note");
update = true;
button.setText("Update");
et_title.setText(note.getTitle());
et_content.setText(note.getContent());
}
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
note.setContent(et_content.getText().toString());
note.setTitle(et_title.getText().toString());
noteDatabase.getNoteDao().updateNote(note);
}
});
}
}
Delete Note
To delete a note object, just invoke the delete method and provide the note object for deletion as the argument.
noteDatabase.getNoteDao().deleteNote(notes.get(pos));
Do not forget to remove object from list which is being used in NoteListActivity to display list and also notify the adapter using adapterObj.notifyDataSetChanged()
Final result after implementing update and delete
Other features
Room offers many other features like LiveData for keeping the data source updated all the time and rxAndroid support for reactive programming.
Conclusion
Check out the sample application repository here. Hopefully this guide introduced you to a lesser known yet useful form of Android application data storage.
Please post your comments, questions, or suggestions in the discussion section below and favorite this guide if you enjoyed it. Thank you for reading!
Advance your tech skills today
Access courses on AI, cloud, data, security, and more—all led by industry experts.